Share it
Treating a groin strain involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation to reduce pain and inflammation. Pain relief, gentle stretching, and gradual return to activity are key for recovery. Seek medical attention if symptoms persist.
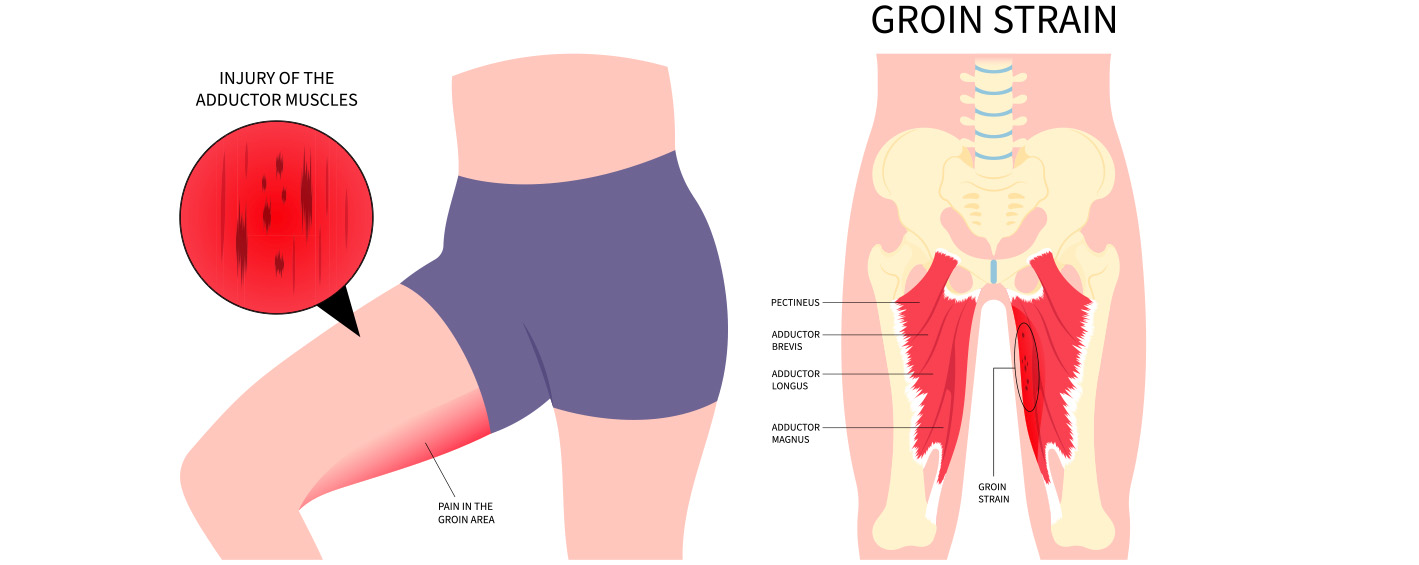
Treating a groin strain involves several steps to promote healing and relieve discomfort:
- Rest: Avoid activities that aggravate the injury to allow the affected muscles to heal properly.
- Ice: Apply ice to the injured area for 15-20 minutes every few hours during the initial 48 hours to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Compression: Use a compression bandage to provide support and reduce swelling. Make sure it's snug but not too tight to avoid restricting blood flow.
- Elevation: Elevate the injured leg above the level of the heart when possible to reduce swelling and promote drainage.
- Pain relief: Over-the-counter pain medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and inflammation.
- Gentle stretching and strengthening exercises: Once the acute pain subsides, perform gentle stretches and strengthening exercises recommended by a healthcare professional to promote healing and prevent re-injury.
- Gradual return to activity: Gradually reintroduce activities and sports once the pain has subsided and range of motion has improved. Start with low-impact exercises and gradually increase intensity and duration.
If the pain persists or worsens despite self-care measures, or if you experience severe pain, swelling, or difficulty walking, it's essential to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment, which may include physical therapy or other interventions tailored to your specific condition.